By Lan Zou (WG SA5 Chair)
First published December 2024, in Highlights Issue 09
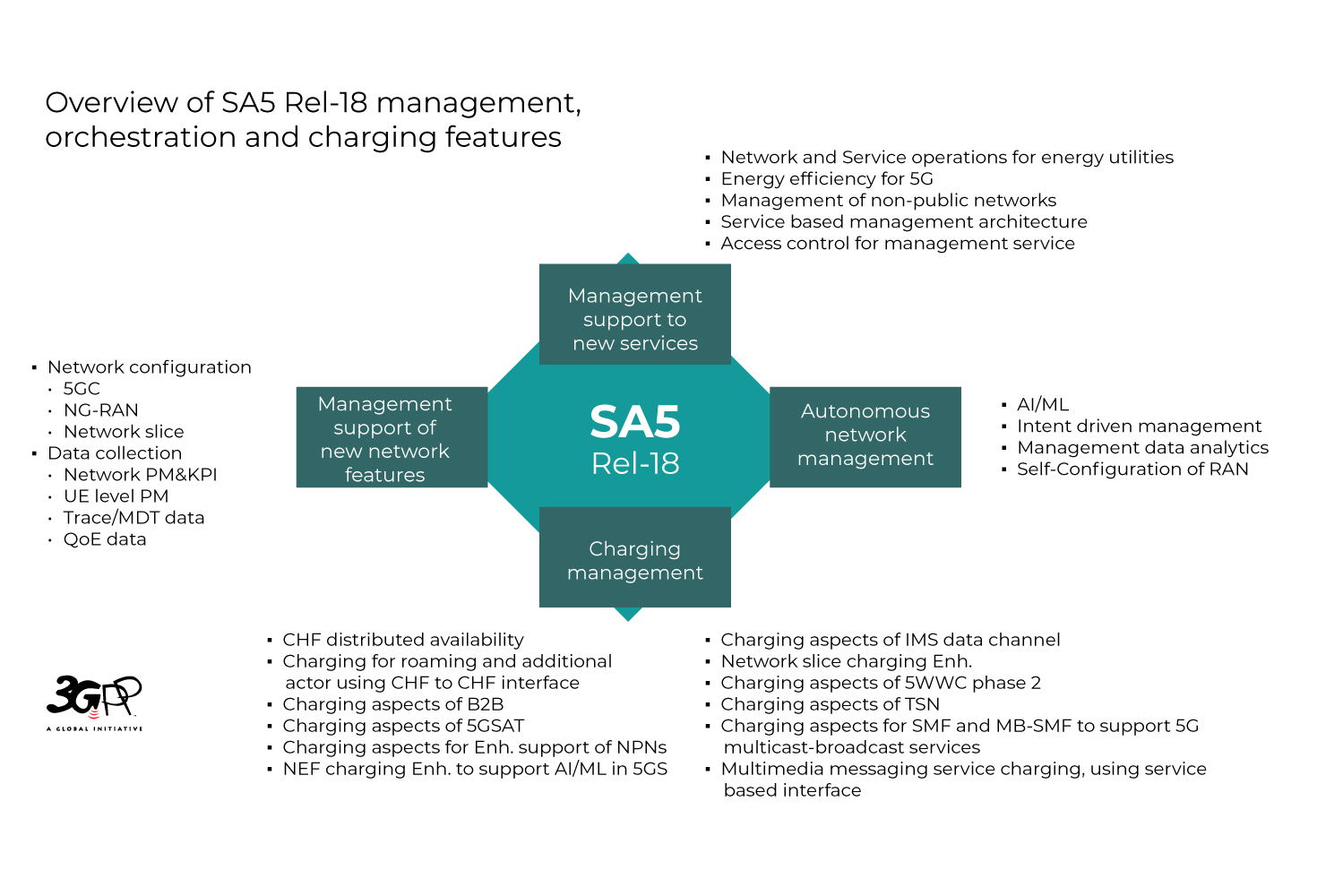
3GPP initiated discussions on 5G in Rel-15. Since then, while more and more network features have been introduced in to the specifications, more management features have also been specified. 3GPP officially published Release 18 (Rel-18) in March 2024. Rel-18 new management features can be classified according to the following four aspects:
- Management support of new network features
- Autonomous network management
- Management support to new services
- Charging management
Management support of new network features:
The management support to new network features in multi-vendor scenario includes network configuration and data collection from the network.
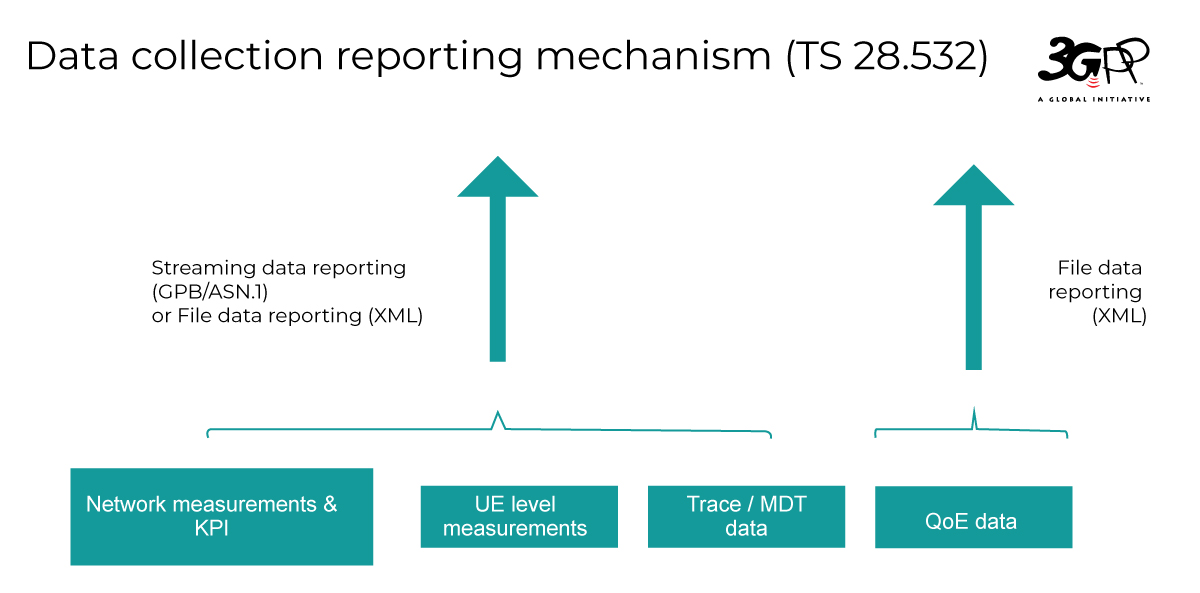
Data collection from the network includes specifying new network measurements and KPI, UE level measurements, QoE data, trace data and corresponding mechanisms for data collection.
The following new measurements for monitoring network performance and KPI are standardized:
RAN related measurements & KPI:
- RSRP measurements: SRS-RSRP measurement,support monitoring of remote interference
- UE throughput measurements: Average DL UE buffered Throughput per DRB,UE throughput of Dedicated BWP
- Delay related measurement: downlink delay to support NTN, one way packet delay between PSA UPF and UE supports satellite backhaul, Distribution of DL GTP packet delay between PSA UPF and NG-RAN, Distribution of UL delay between NG-RAN and UE, Mean interruption time interval for 5QI, air interface UL/DL average efficiency, Average air-interface efficiency achievable per UE
- Packet loss measurements: DL Packet Loss rate on Uu
- Paging measurements: Positive Paging Rate, NG-RAN Initiated paging records
- Mobility management: Conditional PSCell Change
- Connection related measurements: Idle-state RRC release, multi-access PDU Connectivity, Handover per beam-cell pair for inter-system mobility, numbers of DRB setup for Dual Connectivity
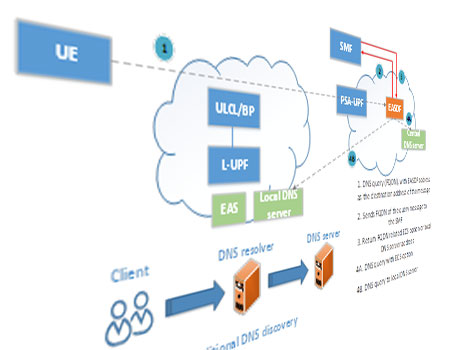
- EES related measurements: EEC Registration, EAS discovery failure
- Reliability related measurements: Packet transmission reliability KPI in UL/DL on F1-U
- Radio resource measurements: Distribution of PDCCH CCE PRB Usage, proportion of time domain resources, Network and Service Operations for Energy Utilities, NgU data volume, connected mode power saving Wake-Up Signal functionality, peak PRB usage per PLMN, PRB Usage per SSB, Distribution of Scheduled PUSCH/PDSCH PRBs, MIMO Layers Coverage Map per UE and PRB
- Time advance measurement: Timing Advance per SS-RSRP and AOA ranges
- GTP capacity measurements: Average DL GTP packet delay between PSA UPF and NG-RAN, Distribution of DL GTP packet delay between PSA UPF and NG-RAN
5GC related measurements & KPI:
- 5G LAN measurements: The performance measurements and KPIs for SMF session management, SMF N4 interface measurements, UPF N3 interface measurements, UPF QoS flow measurements and UPF N19 interface measurements are enhanced to include subcounters for 5G VN group communication.
- NWDAF related measurements: NWDAF analytics service statistics, NWDAF service failure statistics, Measurements related to the coordination between multiple NWDAFs, NWDAF service provisioning statistics, NWDAF Data Collection measurements, NWDAF ML model provision service and NWDAF ML model training service measurements, measurements on coordination between multiple NWDAFs.
UE level measurements: Average DL packet delay between PSA UPF and UE for a QoS flow, Average UL/DL packet delay between PSA UPF and NG-RAN for a QoS flow, Average delay DL air-interface, Average delay DL in gNB-DU, Average delay DL on F1-U, Average delay DL in CU-UP, UL PDCP packet average delay, Average delay UL on over-the-air interface, Average RLC packet delay in the UL, Average PDCP re-ordering delay in the UL, DL Packet Loss Rate on Uu, Packet loss for split gNB deployment scenario, UE throughput, UE Data Volume.
The following enhancement on data collection reporting mechanisms are supported:
MDT data collection mechanism enhancement: Based on the existing MDT data collection mechanism, operators could further select MDT measurement names that are subject to user consent to be activated/deactivated.
Enhancement of QoE Measurement Collection: The QoE Measurement Collection enables collection of application layer measurements from the UE for specified end user service type. The supported service types are Streaming services, MTSI services and VR services with corresponding new measurements. Based on the existing QoE data collection mechanism, operator could further configure RAN visible QoE Metrics. Mechanism to support signaling based QoE activation in NG-RAN is introduced.
Network configuration capability includes specifying the corresponding network resource models and enhancement of management operations. CRUD operations as generic management operations are normally used to manage the lifecycle of network resource model since Rel-15. In order to support interoperability in a multi-vendor scenario, the following configurations are standardized:
Core network configuration: 5G Core managed NFs Profile, UDR Function, UDM Function, PCF Function, NSSF Function, UPF Function, NSSAAF Function, EASDF Function, AF Function, LMF Function, SMSF Function, UDSF Function, SEPP Function, SCP Function, NWDAF Function, NSACF Function, NEF Function, AUSF Function, DCC Function, MFAF Function, CHF Function, GMLC Function, TSCTSF Function, AANF Function, BSF Function, MBSMF Function, MBUPF Function, NRF Function, MNPF Function, enhanced data model for AmfInfo, SmfInfo to support satellite backhaul and 5G LAN.
RAN configuration: radio network sharing modeling, NTN Function, BWPset configuration, NG-RAN 5QI configuration.
Network slicing and other configuration: network slicing isolation Profile, transport entry point model, scheduled slice availability, asynchronous lifecycle management operations for network slicing.
Autonomous network management
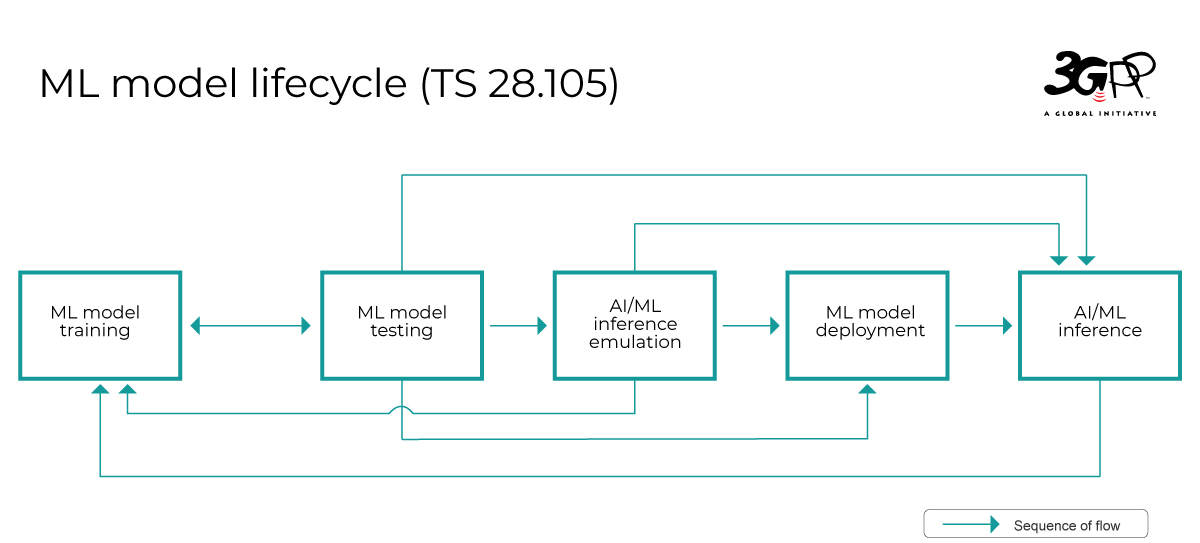
AI/ML management specifies AI/ML management related terminology and definitions, a general management framework for ML model lifecycle (i.e., model training and testing, emulation, deployment, and inference), various management deployment scenarios, AI/ML lifecycle management capabilities including OpenAPIs for ML training, AI/ML emulation, ML model deployment and AI/ML inference. With regard to AI/ML functionalities in the RAN, the management of NG-RAN AI/ML-based distributed Network Energy Saving, NG-RAN AI/ML-based distributed Mobility Optimization, NG-RAN AI/ML-based distributed Load Balancing have been specified in Rel-18.
Intent driven Management Service for Mobile Network specifies intent driven management capabilities for managing radio network and core network in coordinated manner. In the RAN energy saving scenario, operator can provide energy consumption targets and RAN UE throughput targets for selected geographical area, enforce the context for execution, evaluate and adjust targets when needed. The automated system continuously monitors the network performance and energy consumption information, adjusts accordingly to achieve the optimal balance between energy saving effect and service experience by utilizing intelligent mechanisms. With intent driven radio capacity performance assurance, operators can express expected network throughput capacity as target. The operator can also express expected 5GC network capacity targets in a standard way for delivering new 5GC network and system will try its best to achieve the best performance according to the desired intent. Query capability is also provided through which the operator can obtain the supported targets for each intent handling functions and select the proper intent handling function to execute the intent handling process. 3GPP defined intent driven management framework is flexible and easy to be extended for new features.
To facilitate the end-to-end intent driven solution, the two Intent-driven deployment scenarios are shown in TS 28.312, as potential examples utilizing 3GPP defined intent solution to support requests from the communication service customers.
Management Data Analytics (MDA) specifies analytics capabilities to support prediction statistics, NF resource utilization and 5GC congestion analysis.
The MDA is a management functionality that utilizes the collection of current and historical management and network data including e.g., communication service, slicing, management and/or network functions data to perform analytics that could enable intelligent and automated network operations and service assurance. MDA capability allows consumer to request and obtain analytics outcome related to a specific use case (MDA type).
The new use cases and corresponding solutions specified in Rel-18 includes Prediction and statistics of Mobility management performance related predictions, Coverage related predictions, SLS prediction, Critical maintenance management related predictions and Energy saving predictions, physical and virtualized NF resource utilization analysis, and 5GC Control plane congestion analysis. Analytic coordination across multiple domains are also supported.
Self-Configuration of RAN Network Entities (NE) specifies the operators controlled self-configuration process of RAN NEs. With operator provided policy and planned data, RAN NE can be taken to a state ready to carry traffic using self-configuration process in an automated manner. Self-configuration process includes four major steps: generate RAN NE configuration data based on operators’ inputs, download and activate software, download and activate configuration data, self-test. Self-configuration process also provides the capability for operators to more the progress and intervene the automated process execution when needed with standardized solution.
Support to new services
- Enhancements of EE for 5G specifies new 5G network EE measurements include energy consumption of Virtualized Network Functions (VNF) and new Energy Consumption KPIs for virtual compute resources.
- Network and Service Operations for Energy Utilities (NSOEU) is a feature that exposes management information and capabilities from the 5G system to energy utility operators to achieve higher service availability.
- Management of non-public networks (NPN) specifies the requirements and solutions for key aspects of NPN management.
- Enhancement of Service based management architecture (SBMA) provides overview of 5G management specifications, management capabilities, and collaboration with other industry groups from management architectural perspective. New advertising NRM properties capability allows operators to obtain supported configurable properties from providers in a multi-vendor environment.
- Access control for management service introduces the access control capabilities for Management Services.
Charging management
Charging support of new network features and services:
Charging aspects of 5GSAT specifies the Satellite access and satellite backhaul charging, in which operator can deploy and monetize the new business and charging scenarios about the integration with the Satellite/NTN (Non-Terrestrial Network).
Charging Aspects for Enhanced Support of Non-Public Networks specifies the data connectivity and network access usage charging for Standalone Non-Public Network (SNPN) and Public network integrated NPN (PNI-NPN). Operator can monetize the deployment of dedicated and reliable private networks.
NEF Charging enhancement to support AI/ML in 5GS, specifies charging aspect about exposure of 5GC information to authorized 3rd party for Application AI/ML operations, which benefit and enhance the exposure capabilities of operators.
Charging Aspects of IMS Data Channel, specifies Charging Aspects for Enhanced Support of Non-Public Networks new business model.
Network Slice Charging enhancement, help the operators can provide variety and new 5GA business and charging scenarios based on the multiple dimensions, including:
- Charging Aspects for NSSAA: monetize Network Slice(s) assigned to third-party providers based on allowing such third-party to grant authorization or not to individual UEs for accessing a particular network slice via NSSAA.
- Charging Aspects of Network Slicing Phase 2: Network Slice level new criteria for charging Network Slices usage, allowing Operators to monetize Network Slice(s) assigned to third-party providers (i.e. Network Slice Tenant) controlling of UE access and the Network Slice Tenant Charging based on the consumer CCS and Business CCS interactions.
- Network Slice Replacement charging: Operators can monetize the network slice (instances) replacement scenarios.
- Charging enhancement for Network Slice based wholesale in roaming: network slice roaming retails and wholesale charging for Home PLMN and visited PLMN.
Charging Aspects of 5WWC phase 2 specifies 5WWC enhance charging based on the differentiated support for UE(s) behind an RG. The operators could provide more refined and accurate charging for the customers.
Charging Aspects of TSN specifies the time Sensitive Networking charging for supporting the integrated between 5GS and vertical new business and charging scenarios.
Charging Aspects for SMF and MB-SMF to Support 5G Multicast-broadcast Services, specifies the unicast, multicast and broadcast charging for supporting operators to provide new 5G MB services.
Multimedia Messaging Service Charging using service-based interface, specifies the MMS charging for supporting operators to provide new 5G MMS services.
New Charging management capabilities:
CHF Distributed Availability describes the Centralized and Local/Edge CHF deployment, which supports the flexible distributed deployment options for operators.
Charging for roaming and additional actor using CHF to CHF interface describes the new LBO roaming charging architecture, which provides optional inter CHF commutations for operators, including the Home MNO, visited MNO and MVNO retails and wholesale charging.
Charging Aspects of B2B describes the common B2B charging architecture and charging principle, which helps the operators can provide the communication service for the customer subscriber and business subscriber more conveniently.


 Technology
Technology