Page 5 - 3GPP_Highlights_Issue_5_WEB
P. 5
A new logical entity, called the AKMA Anchor Function (AAnF) secure the communication between the UE and the application
has been introduced to support the AKMA feature. From the server, leveraging the highly secure HPLMN based primary
KAUSF, the AUSF generates AKMA key KAKMA and sends it to authentication. Please note, there is no separate authentication
the AKMA Anchor function AAnF. When UE tries to connect of the UE to support AKMA functionality. Instead, AKMA reuses
to an application server, the UE provides the AKMA temporary the 5G primary authentication procedure for the sake of implicit
identifier to the application server. Based on this temporary authentication for AKMA services. Figure-2 above provides the
identifier, the application server interacts with the AAnF to architecture (a) where the Application Function (AF) is within
receive the specific session key KAF and UE identifier. The AF the 5GC and part of the PLMN, whereas (b) provides the scenario
can use received session key KAF or further derive the keys where Application Function (AF) is outside the 5GC and the
based on the session key KAF to secure the communication Application Function (AF) interacts with AKMA Anchor Function
between the UE and the application server. Thus AKMA provides (AAnF) via the Network Exposure Function (NEF).
a reliable framework for applications to authenticate the UE and
AKMA Procedures:
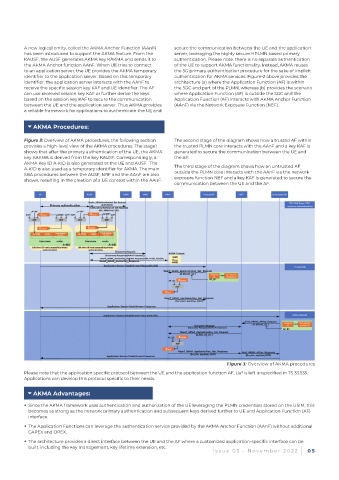
Figure 3: Overview of AKMA procedures, the following section The second stage of the diagram shows how a trusted AF within
provides a high-level view of the AKMA procedures. The stage1 the trusted PLMN core interacts with the AAnF and a key KAF is
shows that after the primary authentication of the UE, the AKMA generated to secure the communication between the UE and
key KAKMA is derived from the key KAUSF. Correspondingly, a the AF.
AKMA Key ID A-KID is also generated at the UE and AUSF. The
A-KID is also used as a temporary identifier for AKMA. The main The third stage of the diagram shows how an untrusted AF
SBA procedures between the AUSF, NRF and the AAnF are also outside the PLMN core interacts with the AAnF via the network
shown, resulting in the creation of a UE context within the AAnF. exposure function NEF and a key KAF is generated to secure the
communication between the UE and the AF.
Figure 3: Overview of AKMA procedures
Please note that the application specific protocol between the UE and the application function AF, Ua* is left unspecified in TS 33.535.
Applications can develop this protocol specific to their needs.
AKMA Advantages:
• Since the AKMA framework uses authentication and authorization of the UE leveraging the PLMN credentials stored on the USIM, this
becomes as strong as the network primary authentication and subsequent keys derived further to UE and Application Function (AF)
interface.
• The Application Functions can leverage the authentication service provided by the AKMA Anchor Function (AAnF) without additional
CAPEX and OPEX.
• The architecture provides a direct interface between the UE and the AF where a customized application-specific interface can be
|
built, including the key management, key lifetime extension, etc.
Issue 05 - No v ember 2 0 22 05