Page 21 - Highlight_Issue_3_final_web
P. 21
Addressing the Future continued...
These conversions will allow future IPv6-only configurations for primary points out IPv6 Enhanced Innovations as the solutions.
Access Point Names (APNs), simplifying the Packet Core and improving
the scalability of the network. The conclusion is that IPv6 is ready to go, especially for the mobile
Internet and the mobile vertical ecosystems, helping unleash the full
IPv6 migration challenges and solutions potential of 5G.
The primary IPv6 migration challenge is the IPv6 support within
current equipment. Typically, it hasn’t been possible to justify replacing References:
equipment just to introduce IPv6. The smoother upgrade solution has [1] IAB Statement on IPv6 (2016, 11)
been to mandate IPv6 support for new devices that replace devices as
they reach the end of their life cycle. [2] ARCEP - Annual barometer of the transition to IPv6 in France (2020, 12)
The next challenge is the lack of IPv6 knowledge and experience. IPv6 [3] ETSI GR IPE 001 - IPv6 Enhanced Innovation (IPE); Gap Analysis (2021, 08)
is not an IPv4 clone with just bigger IP addresses. These protocols are
significantly different. Hence, some efforts to gain needed knowledge The author: Eduard Vasilenko is a Senior Architect, Europe
are mandatory. ETSI did a comprehensive analysis for potential gaps Standardization & Industry Development Department at Huawei Europe.
that may create challenges for IPv6 deployment [3]. The document also The article was reviewed by Latif Ladid, IPv6 Forum President.
DRIVING DATA TO DELIVER
CONNECTED VEHICLE SERVICES
By Said Tabet, AECC
The Automotive Edge Computing Consortium (AECC) white paper, candidate solutions that will satisfy AECC requirements and
Distributed Computing in an AECC System provides an overview capture potential gaps to be addressed by connected vehicle
of distributed computing and the mobility services requirements stakeholders.
for connected vehicle service implementations.
The AECC recommendations made to vehicle OEMs, MNOs and
The document also provides initial solution profiling, to analyze the service providers will provide ways to optimize
existing technologies from standards organizations such as the service offerings.
3GPP and open source communities. The process identifies
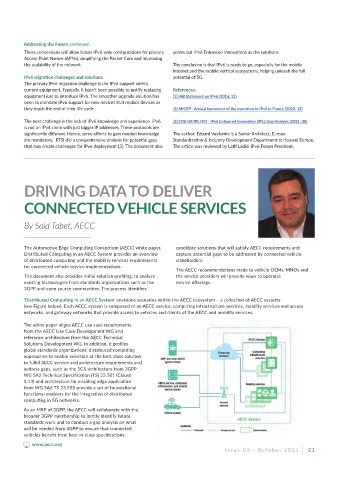
‘Distributed Computing in an AECC System’ envisions scenarios within the AECC ecosystem – a collection of AECC systems
(see Figure below). Each AECC system is composed of an AECC service, computing infrastructure services, mobility services and access
networks, and gateway networks that provide access to vehicles and clients of the AECC and mobility services.
The white paper aligns AECC use case requirements
from the AECC Use Case Development WG and
reference architecture from the AECC Technical
Solutions Development WG. In addition, it profiles
global standards organizations’ distributed computing
approaches to enable selection of the best class solution
to fulfill AECC service and architecture requirements and
address gaps, such as the 5GS architecture from 3GPP
WG SA2 Technical Specification (TS) 23.501 (Clause
5.13) and architecture for enabling edge application
from WG SA6 TS 23.558 provide a set of foundational
functional enablers for the integration of distributed
computing in 5G networks.
As an MRP of 3GPP, the AECC will collaborate with the
broader 3GPP membership to jointly identify future
standards work and to conduct a gap analysis on what
will be needed from 3GPP to ensure that connected
vehicles benefit from best-in-class specifications.
www.aecc.org
|
I ssue 03 - O ct ober 2021 21