Page 12 - Highlight_Issue_3_final_web
P. 12
TECHNICAL HIGHLIGHTS
ENHANCED SUPPORT OF
INDUSTRIAL IOT IN THE
5G SYSTEM (REL-17)
By Devaki Chandramouli, Work Item Rapporteur
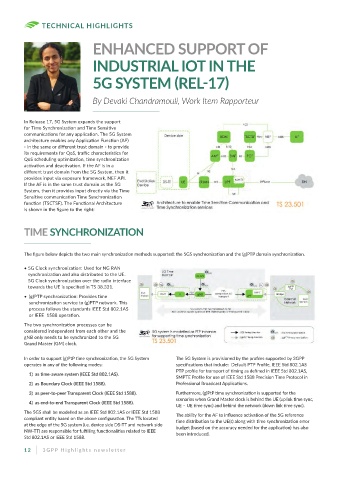
In Release 17, 5G System expands the support
for Time Synchronization and Time Sensitive
communications for any application. The 5G System
architecture enables any Application Function (AF)
- in the same or different trust domain - to provide
its requirements for QoS, traffic characteristics for
QoS scheduling optimization, time synchronization
activation and deactivation. If the AF is in a
different trust domain from the 5G System, then it
provides input via exposure framework, NEF API.
If the AF is in the same trust domain as the 5G
System, then it provides input directly via the Time
Sensitive communication Time Synchronization
function (TSCTSF). The Functional Architecture
is shown in the figure to the right:
TIME SYNCHRONIZATION
The figure below depicts the two main synchronization methods supported: the 5GS synchronization and the (g)PTP domain synchronization.
• 5G Clock synchronization: Used for NG RAN
synchronization and also distributed to the UE.
5G Clock synchronization over the radio interface
towards the UE is specified in TS 38.331.
• (g)PTP synchronization: Provides time
synchronization service to (g)PTP network. This
process follows the standards IEEE Std 802.1AS
or IEEE 1588 operation.
The two synchronization processes can be
considered independent from each other and the
gNB only needs to be synchronized to the 5G
Grand Master (GM) clock.
In order to support (g)PtP time synchronization, the 5G System The 5G System is provisioned by the profiles supported by 3GPP
operates in any of the following modes: specifications that include: Default PTP Profile, IEEE Std 802.1AS
PTP profile for transport of timing as defined in IEEE Std 802.1AS,
1) as time-aware system (IEEE Std 802.1AS).
SMPTE Profile for use of IEEE Std 1588 Precision Time Protocol in
2) as Boundary Clock (IEEE Std 1588). Professional Broadcast Applications.
3) as peer-to-peer Transparent Clock (IEEE Std 1588). Furthermore, (g)PtP time synchronization is supported for the
scenarios when Grand Master clock is behind the UE (uplink time sync,
4) as end-to-end Transparent Clock (IEEE Std 1588).
UE – UE time sync) and behind the network (down link time sync).
The 5GS shall be modelled as an IEEE Std 802.1AS or IEEE Std 1588 The ability for the AF to influence activation of the 5G reference
compliant entity based on the above configuration. The TTs located time distribution to the UE(s) along with time synchronization error
at the edge of the 5G system (i.e. device side DS-TT and network side budget (based on the accuracy needed for the application) has also
NW-TT) are responsible for fulfilling functionalities related to IEEE been introduced.
Std 802.1AS or IEEE Std 1588.
|
12 3GPP H ighligh ts ne w sle tt er